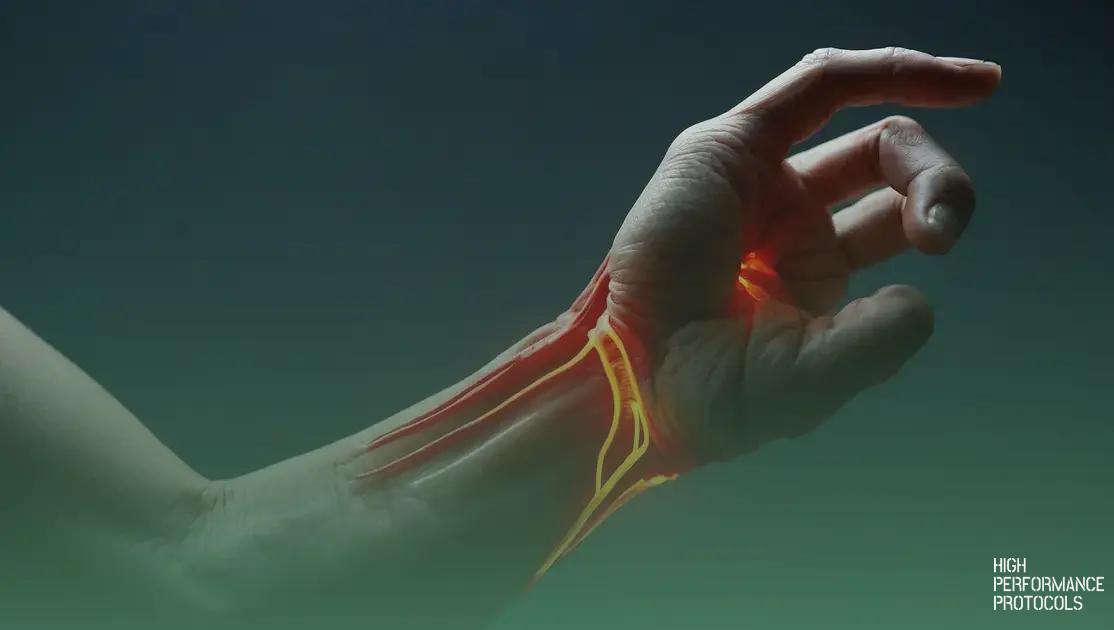
Median nerve entrapment neuropathy occurs when the median nerve is compressed, leading to symptoms such as pain, tingling, and numbness in the hand; effective treatments include physical therapy, medications, and, if necessary, surgical intervention.
Median nerve entrapment neuropathy can be a frustrating condition, leading to discomfort that can affect daily activities. Have you ever experienced tingling in your fingers or pain in your wrist? Understanding this condition is essential for anyone looking to find effective relief.
What is median nerve entrapment neuropathy?
Median nerve entrapment neuropathy is a condition that occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm of the hand, becomes compressed. This nerve is responsible for the sensation in the thumb, index, and middle fingers, as well as controlling some wrist and finger movements.
The entrapment often occurs at the wrist, where it passes through a tunnel of ligaments known as the carpal tunnel. Symptoms can include pain, tingling, numbness, or weakness in the affected hand. These sensations can interfere with daily tasks like writing or holding objects.
Several factors can contribute to the development of this condition, including repetitive wrist movements, injury, or conditions like diabetes that may affect nerve health. Understanding the causes is key to effective treatment and prevention.
Common causes of median nerve entrapment
There are several common causes of median nerve entrapment that can lead to discomfort and potential damage to the nerve. Understanding these causes can help in both prevention and treatment.
One of the primary causes is repetitive hand movements, often seen in jobs that require frequent typing or using hand tools. This repetitive motion can create pressure on the median nerve.
Another significant factor is injury. A direct impact to the wrist can cause swelling and inflammation, leading to compression of the nerve.
Medical conditions also play a role. Conditions such as diabetes can impair nerve function, while thyroid disorders may lead to an overall increase in body fluid, adding pressure to the median nerve.
Pregnancy is another common cause of median nerve entrapment. Hormonal changes can result in swelling around the wrist, contributing to nerve compression.
Obesity is also linked to this condition. Extra weight can lead to increased pressure on nerves and may facilitate the development of symptoms.
Lastly, maintaining poor posture while performing tasks can exacerbate the likelihood of developing median nerve entrapment. Being mindful of ergonomic setups can significantly reduce this risk.
Identifying symptoms: tingling and pain
Identifying the symptoms of median nerve entrapment neuropathy is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. The most common symptoms include tingling, pain, and numbness in the hand and fingers.
Tingling sensations often occur in the thumb, index, and middle fingers. This feeling may start as intermittent but can progress to more constant discomfort if left untreated.
Patients may also experience pain that radiates from the wrist to the arm. This pain can worsen at night or during activities that involve repetitive hand movements. Some people find relief by shaking their hands or changing positions, while others may have constant discomfort.
Numbness is another key symptom. It can make it difficult to perform simple tasks like grasping objects or buttoning a shirt. Loss of sensation may also occur, which can impact hand coordination.
As the condition progresses, muscle weakness in the affected hand may develop. Individuals might struggle to lift objects or have difficulty during fine motor activities like writing.
Recognizing these symptoms early can help in seeking appropriate medical advice, leading to timely intervention and better outcomes.
How diagnosis is made: tests and tools
Diagnosing median nerve entrapment neuropathy typically involves a combination of physical examinations, patient history, and specific tests to assess nerve function.
Initially, a healthcare professional will conduct a physical examination. This may include checking for symptoms like tingling, weakness, or numbness in the hands. The doctor may perform a series of maneuvers to provoke these symptoms and assess how the condition affects your daily activities.
Nerve conduction studies (NCS) are crucial tests that measure how quickly electrical signals travel through the median nerve. This test can pinpoint areas of nerve compression and help confirm the diagnosis.
Electromyography (EMG) is another important tool that measures the electrical activity in muscles. It can help determine if there is any damage to the nerve and assess how well muscles react to nerve signals.
In addition to these tests, doctors may also use ultrasound imaging to visualize the median nerve and surrounding structures. This can provide more detailed information about swelling or other changes that may indicate entrapment.
In some cases, an X-ray or MRI may be used to rule out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms, such as fractures or tumors.
Understanding the specific tests and tools used for diagnosis can help patients feel more informed and involved in their treatment journey.
The role of nerve conduction studies
Nerve conduction studies (NCS) are vital for diagnosing median nerve entrapment neuropathy. They help assess how well electrical signals travel through the median nerve, providing crucial information about its function.
During an NCS, small electrodes are placed on the skin over the nerve and muscle. These electrodes send electrical impulses, measuring the speed and strength of the signals. This test is non-invasive and typically takes about 30 to 60 minutes to complete.
A primary purpose of nerve conduction studies is to identify nerve damage or compression. If the median nerve is compressed, the electrical signals will travel more slowly than usual, indicating a problem. This information aids doctors in determining the severity of the entrapment and planning appropriate treatment.
Nerve conduction studies can also help distinguish between different types of nerve issues, such as whether the symptoms are due to median nerve entrapment or other conditions affecting the nerves. This is particularly important because symptoms can overlap with disorders like radiculopathy or peripheral neuropathy.
In summary, nerve conduction studies are an essential diagnostic tool. They provide valuable insights into the function and health of the median nerve, guiding treatment options and patient management.
Treatment options: non-surgical approaches
There are several non-surgical treatment options available for managing median nerve entrapment neuropathy. These approaches aim to relieve symptoms and improve functionality without the need for invasive procedures.
One of the first steps in treatment is often activity modification. Reducing repetitive motions and ensuring ergonomic setups can help decrease pressure on the median nerve. This might include adjusting workstations or using tools that minimize strain.
Physical therapy is another effective option. A trained therapist can design a program that includes stretching and strengthening exercises tailored to your needs. This therapy helps improve wrist mobility and reduces symptoms over time.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help manage pain and inflammation. These medications are commonly recommended for short-term relief.
In some cases, physicians may recommend the use of a wrist splint. Wearing a splint, especially at night, can keep the wrist in a neutral position, reducing pressure on the median nerve and allowing it to heal.
Other treatments may include corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation around the nerve. These injections can provide temporary relief and improve function, especially when combined with physical therapy.
Overall, these non-surgical approaches can be very effective in treating median nerve entrapment neuropathy. They help manage symptoms and improve quality of life without the need for surgery.
The importance of physical therapy in recovery
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the recovery from median nerve entrapment neuropathy. It is designed to improve strength, flexibility, and function in the affected hand and wrist.
A physical therapist will assess your specific condition and create a customized treatment plan. This plan often includes exercises that focus on stretching and strengthening the muscles around the wrist. These exercises help alleviate pressure on the median nerve.
In addition to targeted exercises, physical therapy can help with manual therapy techniques. These techniques include massage and mobilization of the wrist joint, which can promote healing and reduce pain.
Another important aspect of physical therapy is education. Therapists teach patients about proper ergonomics and body mechanics. Understanding how to maintain good posture and limit repetitive movements can prevent further issues.
Patients often find that regular sessions help them regain their range of motion and reduce discomfort. Physical therapy can also enhance blood flow to the area, which supports overall recovery.
Overall, embracing physical therapy is essential for anyone experiencing symptoms of median nerve entrapment. It not only aids in recovery but also encourages a return to daily activities with improved strength and function.
When to consider surgical intervention
While most cases of median nerve entrapment neuropathy can be managed with non-surgical treatments, there are circumstances where surgical intervention becomes necessary. Understanding when to consider surgery is important for effective management of the condition.
If symptoms persist despite consistent non-surgical treatments, such as physical therapy and the use of splints, it may be time to discuss surgical options with a healthcare provider. Prolonged numbness or weakness in the hand can indicate a need for surgery. If these symptoms are significantly impacting daily activities, surgery might be warranted.
Another factor to consider is the severity of nerve damage. Surgical intervention is often recommended when nerve conduction studies show significant impairment of the median nerve. Early surgical treatment can prevent permanent nerve damage and help regain function.
A patient may also consider surgery if they experience severe pain that does not respond to pain management strategies. When pain interferes with quality of life, surgical options should be explored.
Additionally, if neurological exams indicate atrophy or other physical changes in the hand muscles, surgery may be required to alleviate the pressure on the median nerve and restore normal function.
Ultimately, the decision to opt for surgical intervention will depend on individual circumstances. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide the necessary guidance on the best path forward.
Home remedies for symptom relief
For those suffering from median nerve entrapment neuropathy, there are several home remedies that may help alleviate symptoms. These remedies can be used in conjunction with professional treatment or on their own, depending on the severity of the condition.
One common remedy is to apply a cold compress to the wrist. This can reduce swelling and relieve pain. Simply wrap ice in a cloth and apply it to the affected area for 15 to 20 minutes several times a day.
Warm compresses can also be beneficial. Applying heat can help relax the muscles around the nerve and improve circulation. A warm towel or heating pad can provide soothing relief.
Gentle stretching exercises can also be effective. Stretching the muscles in your wrist and hand can help improve flexibility and reduce tension. Exercises like wrist flexor and extensor stretches may offer relief.
Incorporating certain herbal remedies may also aid in symptom relief. Turmeric and ginger are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Adding them to your diet may help reduce inflammation and pain associated with nerve entrapment.
Maintaining a healthy diet rich in vitamins B6 and B12 can support nerve health. Foods like fish, eggs, and leafy greens can provide essential nutrients that help improve symptoms.
Finally, reducing repetitive movements and taking frequent breaks during activities can prevent aggravation of symptoms. Listening to your body’s signals is key to managing discomfort effectively.
Dietary considerations for nerve health
Maintaining a healthy diet is crucial for supporting nerve health, especially for those experiencing median nerve entrapment neuropathy. Certain nutrients play an important role in promoting optimal nerve function.
Including foods rich in vitamin B6 can be very beneficial. This vitamin helps produce neurotransmitters and supports nerve repair. Good sources of vitamin B6 include poultry, fish, potatoes, chickpeas, and bananas.
Vitamin B12 is another key nutrient for nerve health. It is essential for maintaining the myelin sheath, which protects nerves. Foods high in vitamin B12 include meat, dairy products, and fortified cereals.
Omega-3 fatty acids are also important for nerve health. These healthy fats have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce nerve pain and promote healing. You can find omega-3s in fatty fish, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds.
Antioxidant-rich foods can combat oxidative stress and inflammation, which may contribute to nerve damage. Foods such as berries, broccoli, spinach, and nuts are excellent sources of antioxidants.
Staying well-hydrated is also essential for nerve function. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day to support overall health and nerve function.
Finally, limiting processed foods, sugar, and trans fats can also help improve nerve health. These foods can promote inflammation and hinder healing.
Managing pain: medication and alternatives
Managing pain associated with median nerve entrapment neuropathy can involve various medication options and alternative therapies. Understanding these methods is vital for effective symptom relief.
Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. These nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often the first line of defense for managing mild to moderate discomfort.
If pain persists, healthcare providers may prescribe stronger pain medications such as opioids or neuropathic agents like gabapentin or pregabalin. These medications target nerve pain directly and can be effective for patients with more severe symptoms.
Aside from medication, alternative therapies can provide additional relief. Methods such as acupuncture have been shown to help reduce pain and improve function. Many patients find that regular sessions can complement their treatment plan.
Physical therapy is another beneficial option. A therapist can guide patients through exercises specifically designed to relieve pain while improving strength and flexibility in the affected area.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is also valuable for managing chronic pain. This type of therapy helps individuals develop coping strategies to deal with pain and the emotional aspects related to it.
Lastly, lifestyle changes like maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and engaging in regular physical activity can help manage pain effectively. These adjustments promote overall health and can lessen the strain on the median nerve.
Exploring long-term outlook and improvements
The long-term outlook for individuals with median nerve entrapment neuropathy can vary significantly based on several factors, such as the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment.
With appropriate intervention—whether non-surgical or surgical—most patients can expect a significant reduction in symptoms and an improvement in functionality. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial for a positive outcome. If left untreated, symptoms may worsen, leading to potential permanent nerve damage.
Following non-surgical treatments like physical therapy, many patients report lasting benefits that enhance their quality of life. Regular stretching, ergonomic adjustments, and lifestyle changes contribute to ongoing improvements and can help prevent future episodes.
For those who do undergo surgery, the long-term results are often positive. Many patients experience a significant reduction in pain, improved range of motion, and enhanced strength in the affected hand. However, recovery times may vary, and some individuals might need to continue physical therapy to regain full function.
Monitoring ongoing symptoms is also essential. Patients should remain vigilant and communicate with their healthcare provider about any changes or recurring issues. This proactive approach can help manage complications before they escalate.
Overall, with effective treatment and lifestyle adjustments, many individuals can lead normal, active lives despite their diagnosis of median nerve entrapment neuropathy. The journey involves continuous self-care and potentially adapting work and recreational activities to support nerve health.
In summary: Navigating median nerve entrapment neuropathy
Median nerve entrapment neuropathy can be a challenging condition, but understanding its causes and symptoms is the first step towards effective management.
With a variety of treatment options available, from non-surgical methods like physical therapy and medication to potential surgical interventions, many individuals can find relief and regain functionality in their daily lives.
Incorporating lifestyle changes, dietary improvements, and home remedies can further enhance recovery and support long-term nerve health.
It is vital to stay informed and proactive, ensuring regular communication with healthcare providers about any changes in symptoms or new concerns.
By taking these steps, individuals can effectively manage their condition and improve their quality of life, overcoming the challenges posed by median nerve entrapment neuropathy.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Median Nerve Entrapment Neuropathy
What is median nerve entrapment neuropathy?
Median nerve entrapment neuropathy is a condition where the median nerve, which runs through the wrist, becomes compressed, leading to symptoms such as pain, tingling, and numbness in the hand.
What are the common symptoms of this condition?
Common symptoms include tingling, numbness, and pain in the thumb, index, and middle fingers, as well as weakness in the hand.
What non-surgical treatments are available?
Non-surgical treatments include physical therapy, splinting, medication for pain relief, and lifestyle modifications to reduce strain on the wrist.
When should I consider surgery for median nerve entrapment?
Consider surgery if symptoms persist despite non-surgical treatments, or if there is significant nerve damage or weakness affecting daily activities.
Can dietary changes help manage symptoms?
Yes, a healthy diet rich in vitamins B6 and B12, as well as omega-3 fatty acids, can support nerve health and improve symptoms.
What is the long-term outlook for individuals with this condition?
With appropriate treatment, many individuals can expect significant improvement in symptoms and functionality, leading to a better quality of life.

Max is a health and wellness researcher dedicated to optimizing human performance through science-backed protocols. As a contributor to High Performance Protocols, he analyzes the latest medical studies and translates complex research into practical, easy-to-follow strategies for improving energy, longevity, and overall well-being. Passionate about biohacking, nutrition, and evidence-based health solutions, Max Reynolds helps readers navigate the ever-evolving world of health optimization with clarity and precision.